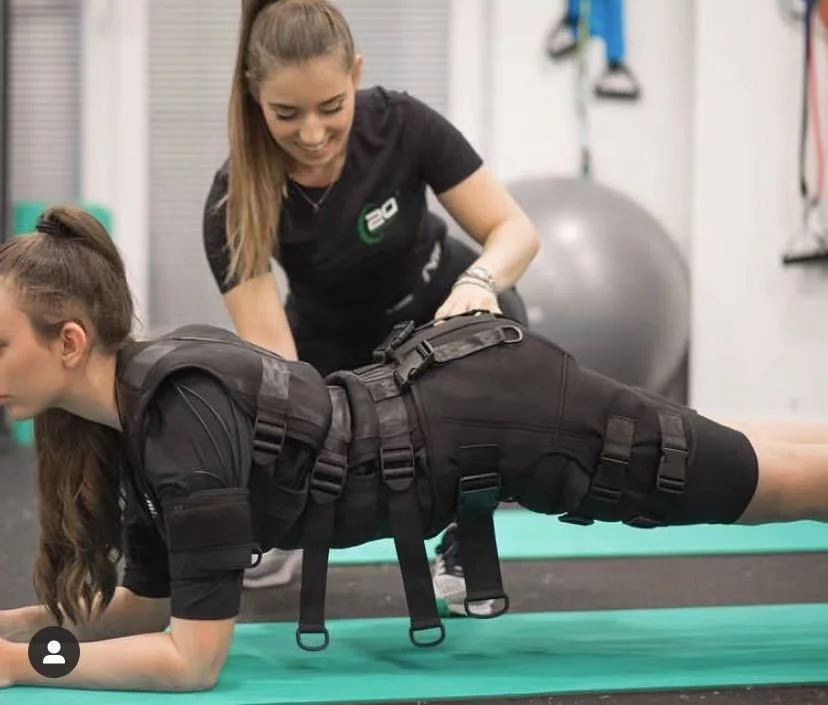
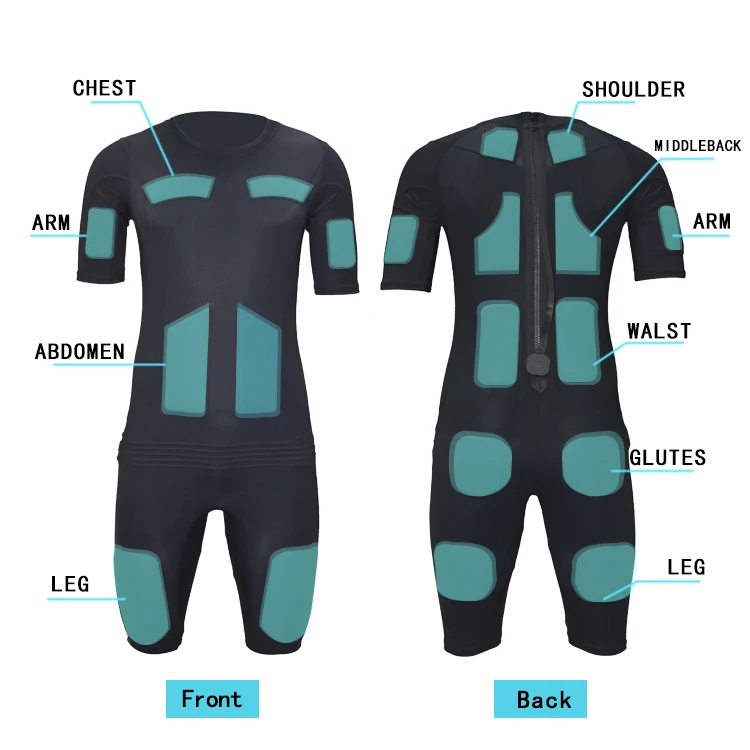
What is the Difference Between a TENS and EMS Machine? Industry Insights Unveiled
The electrotherapy device market has seen rapid growth, driven by rising health awareness and demand for non-invasive solutions. Among the most debated products are TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) and EMS (Electrical Muscle Stimulation) machines. While both utilize electrical pulses, their purposes, mechanisms, and applications differ significantly.
1. Core Functional Differences
TENS: Primarily designed for pain relief, TENS devices send low-frequency electrical pulses (typically 20–120Hz) to sensory nerves, blocking pain signals from reaching the brain. This triggers the release of endorphins, the body's natural painkillers. Common applications include chronic back pain, arthritis, and menstrual cramps.
EMS: Focused on muscle activation and rehabilitation, EMS uses higher-frequency pulses (50–550Hz) to stimulate motor nerves, causing controlled muscle contractions. This mimics voluntary exercise, aiding muscle strengthening, recovery from atrophy, and athletic performance enhancement.
EMS Working Principle:
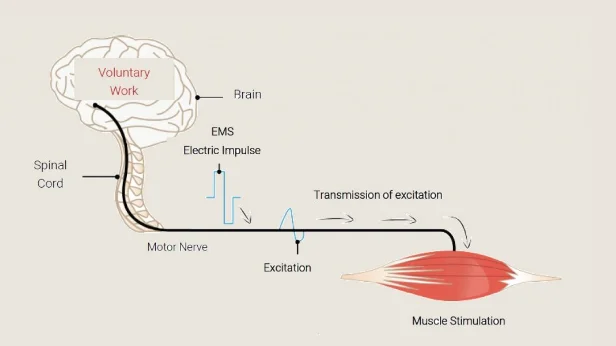
2. Technical Specifications
Pulse Width: TENS operates with narrower pulses (50–300μs), while EMS employs wider pulses (200–400μs) to penetrate deeper muscle layers.
Target Tissues: TENS affects sensory nerves and skin layers, whereas EMS directly engages muscle fibers, activating up to 90% of them-far surpassing traditional workouts.
waveform picture

ems Wave
Cowers Commercial Cleaning Robot Landing Case:China Mobile Software Park

Tens Wave
Cowers Commercial Cleaning Robot Landing Case:China Mobile Software Park
3. Market Applications And Trends
TENS Dominates Pain Management:
Widely adopted in home care and clinics, TENS devices like the Portable 1-Paddle Tesla Stimulator are marketed for conditions like sciatica and post-surgical recovery.
EMS in Fitness and Aesthetics:
EMS machines are popular in gyms and beauty salons for "passive workouts" that build muscle tone and reduce fat. Clinical studies show 16% muscle improvement after 6–8 sessions. Hybrid devices combining EMS with RF (Radio Frequency) further enhance skin tightening, appealing to beauty-conscious consumers.
4. Industry Outlook
The global electrotherapy market is projected to grow at 7.5% CAGR through 2030, with TENS remaining a staple in pain management and EMS expanding into home fitness and rehabilitation. As AI and wearable tech advance, expect smarter devices offering personalized therapy plans and real-time biofeedback.
While TENS and EMS share technological roots, their distinct roles-pain relief versus muscle activation-define separate yet complementary market niches.









